If you frequently make international transactions or have a business that operates globally, you may have come across terms like IBAN and SWIFT codes. These codes are used to facilitate international payments and ensure that money is transferred securely and accurately between banks. In this comprehensive guide, we will break down what IBAN and SWIFT codes are, how to interpret them, and how to use them effectively.
Content Recap:
What are IBAN and SWIFT Codes, and Why are They Important?
An IBAN, or International Bank Account Number, is a unique identifier assigned to bank accounts involved in international transactions. The IBAN contains information about the country, bank, and specific account, making it easier for banks to process cross-border payments. IBANs are used by banks in Europe, the Middle East, and parts of Africa and Asia.
SWIFT, or Society for Worldwide Interbank Financial Telecommunication, codes are a global system used for transferring money between banks. SWIFT codes consist of eight to eleven characters and are used to identify the bank, country, and location of the recipient’s account. Unlike IBANs, which are specific to individual bank accounts, SWIFT codes are assigned to banks themselves.
Both IBAN and SWIFT codes are important for international transactions as they ensure that the correct bank and account are used, reducing the risk of errors and delays in payment processing.
How to Interpret an IBAN: Breaking Down the Different Sections
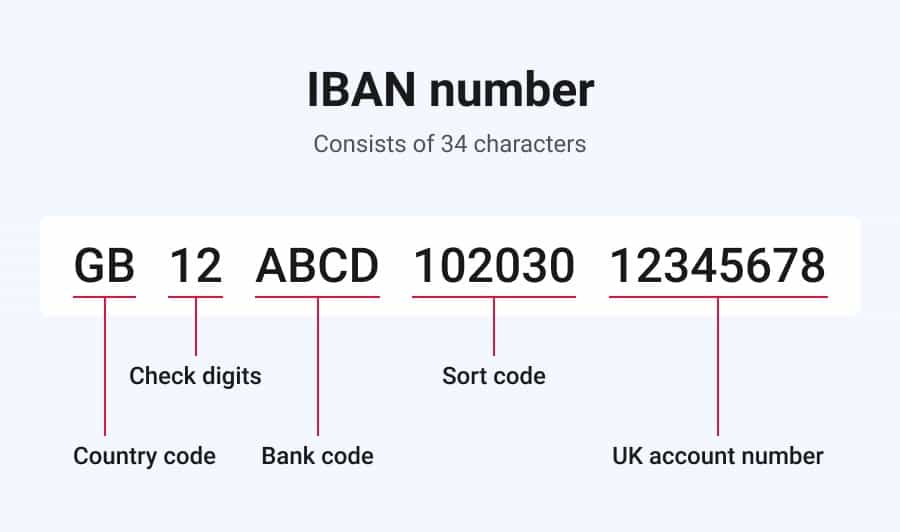
IBANs are made up of a series of alphanumeric characters, typically ranging from 15 to 34 digits depending on the country. Each IBAN contains a country code, check digits, and the bank account number. The specific format of the IBAN varies by country.
The first two characters of the IBAN represent the country code, followed by two check digits. The check digits are used to verify that the IBAN is valid and has been calculated using a specific algorithm. The remaining characters represent the bank and account numbers.
Decoding SWIFT Codes: Understanding the Structure and Format
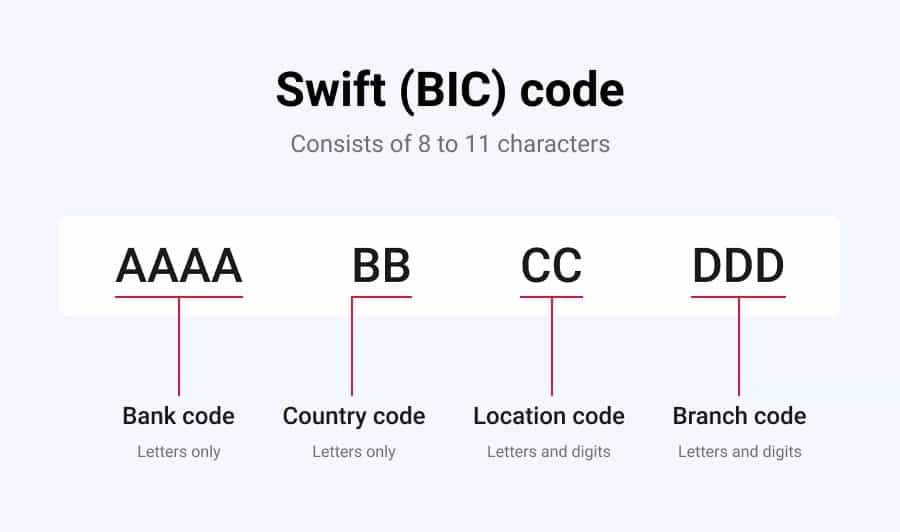
SWIFT codes are also made up of alphanumeric characters and consist of a unique 8-11 character code. The first four characters of the code represent the bank code, followed by two characters for the country code, two for the location code, and three for the branch code. However, not all SWIFT codes contain all of these sections.
The first four characters of the SWIFT code are assigned to the bank and help to identify the financial institution that the code is associated with. The country code and location code provide information about the country and city where the bank is located. Finally, the branch code is used to identify a specific branch of the bank.
IBAN vs. SWIFT: What’s the Difference, and When to Use Each
IBANs and SWIFT codes are both used for international transactions, but they serve different purposes. IBANs are used to identify individual bank accounts involved in international payments, while SWIFT codes identify the bank itself.
If you are making an international payment, you will typically need both the IBAN and SWIFT codes for the recipient’s bank. The IBAN is used to ensure that the correct bank account is credited with the payment, while the SWIFT code is used to identify the bank.
How to Generate an IBAN or SWIFT Code: A Step-by-Step Guide
What is an IBAN Code?
IBAN stands for International Bank Account Number. It is a unique identifier for a bank account that is used in international money transfers. IBAN codes are composed of a country code, two check digits, and a bank account number. The format of IBAN codes varies by country, but they are typically between 16 and 34 characters long.
How to Generate an IBAN Code
To generate an IBAN code, you’ll need to know the recipient’s bank account number and the bank’s routing number. You can generate an IBAN code using an online IBAN generator or by contacting your bank. Some banks also include IBAN codes on account statements.
What is a SWIFT Code?
SWIFT stands for Society for Worldwide Interbank Financial Telecommunication. A SWIFT code is a unique identifier for a bank and is used in international money transfers. SWIFT codes are composed of either 8 or 11 characters and include a bank code, a country code, a location code, and a branch code.
How to Generate a SWIFT Code
To generate a SWIFT code, you’ll need to know the recipient’s bank’s SWIFT code. You can find a bank’s SWIFT code by searching online or by contacting the bank directly. Some banks also include SWIFT codes on account statements.
What are the Differences Between IBAN and SWIFT Codes?
IBAN codes are used to identify individual bank accounts, while SWIFT codes are used to identify banks themselves. IBAN codes are used primarily in Europe, the Middle East, and some countries in Africa and Asia, while SWIFT codes are used worldwide. IBAN codes are longer than SWIFT codes and contain more detailed information about the bank account.
Why are IBAN and SWIFT Codes Important?
IBAN and SWIFT codes are important because they ensure that international money transfers are processed correctly. Without these codes, it can be difficult to identify the correct bank and bank account, which can lead to delays or even lost funds. By using IBAN and SWIFT codes, you can ensure that your money is transferred quickly and securely.
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Using IBAN and SWIFT Codes
- Incorrect Formatting: IBANs and SWIFT codes are typically long and contain specific characters, which can lead to errors when typing them out. Make sure to double-check the codes and ensure that they are in the correct format before initiating a transfer.
- Using the Wrong Codes: IBANs and SWIFT codes are unique to each bank and are used to identify the bank and account holder during a transaction. Using the wrong codes can result in the transfer being rejected or sent to the wrong account.
- Not Updating the Codes: Banks may change their IBAN or SWIFT codes due to mergers, acquisitions, or rebranding. Failing to update these codes can result in transactions being declined or delayed.
- Using Outdated Information: It’s crucial to use the most up-to-date information when sending and receiving international transfers. Failure to do so can result in transactions being rejected or returned.
- Not Confirming with the Recipient: Before initiating a transfer, it’s best to confirm the recipient’s bank details, including their IBAN and SWIFT codes. This can help prevent errors and ensure that the transfer is processed correctly.
- Not Understanding the Fees: Banks and financial institutions may charge fees for international transfers, which can vary depending on the amount, destination, and currency. Make sure to understand the fees associated with the transfer and account for them when sending or receiving funds.
- Using Unverified Third-Party Services: Third-party services may claim to offer lower fees or faster transfer times than traditional banks. However, it’s important to ensure that these services are legitimate and secure before using them for international transfers.
- Not Including Relevant Information: When sending or receiving international transfers, it’s crucial to include relevant information such as the purpose of the transaction, the sender’s contact information, and any reference numbers provided by the bank.
- Not Considering Currency Exchange Rates: When sending funds to another country, the exchange rate between currencies can have a significant impact on the amount received by the recipient. It’s essential to consider the current exchange rate and any associated fees before initiating a transfer.
- Not Checking Transfer Limits: Banks and financial institutions may have transfer limits in place for international transactions. It’s important to check these limits before initiating a transfer to ensure that the amount being sent falls within the allowed range.
